Introduction
The <legend> element in HTML is used in conjunction with the <fieldset> element to provide a caption or description for a group of related form elements. The <fieldset> element is used to group and semantically associate form controls, and the <legend> element serves as a title or explanatory text for that group.
Here’s an example of how <fieldset> and <legend> are used together:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<fieldset>
<legend>Contact Information</legend>
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name">
<br>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email">
<!-- Other form controls can go here -->
</fieldset>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>Output :
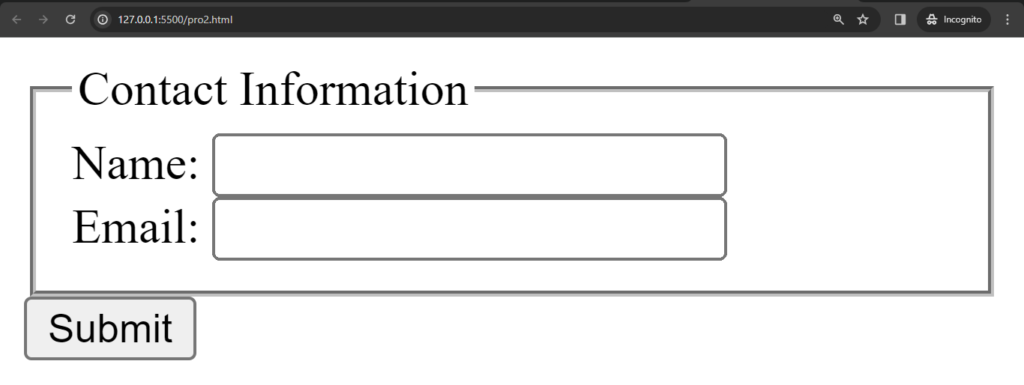
In this example:
- The
<fieldset>element groups together the form controls related to contact information. - The
<legend>element provides a title, “Contact Information,” for the group of form controls.
This is particularly useful for creating more structured and accessible forms. The use of <legend> helps users understand the context of the form controls within the fieldset, especially when there are multiple sections or groups of controls on a form.
It’s important to note that the <legend> element should be the first child of the <fieldset> element. Additionally, using <fieldset> and <legend> is optional, and they are typically used when there’s a need to semantically group related form controls.
Uses of <legend> tag :
Here are some common uses and benefits of the <legend> tag:
1. Grouping Form Controls: Grouping related form controls under a common title, making the form more organized and providing context to the user.
<form>
<fieldset>
<legend>Contact Information</legend>
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name">
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email">
<!-- Other form controls can go here -->
</fieldset>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
2. Accessibility: The <legend> tag helps screen readers and other assistive technologies provide a better understanding of the purpose and context of the grouped form controls.
3. Styling: Developers can style the <legend> element to enhance the visual presentation of the form. For example, changing the font size, color, or adding background styles.
4. Form Structure: Dividing a form into logical sections, such as shipping and billing addresses, for better organization and user experience.
<form>
<fieldset>
<legend>Shipping Address</legend>
<!-- Shipping address form controls -->
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<legend>Billing Address</legend>
<!-- Billing address form controls -->
</fieldset>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
5. Internationalization: Providing a <legend> for each fieldset can aid in internationalization efforts by making the form structure more understandable across different languages.
It’s important to note that while the <legend> tag is a useful tool for organizing and enhancing the accessibility of forms, it is not mandatory for every form. It is most beneficial in situations where grouping form controls under a common title adds clarity to the form structure.
