Introduction
The ‘<datalist>‘ element in HTML is used to provide a predefined list of options for other controls, typically used in conjunction with the ‘<input>‘ element. It allows users to choose from a set of predefined options while still allowing them to enter custom values.
Here’s a simple example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<label for="browser">Choose a browser:</label>
<input list="browsers" id="browser" name="browser" />
<datalist id="browsers">
<option value="Chrome">
<option value="Firefox">
<option value="Safari">
<option value="Edge">
<option value="Opera">
</datalist>
</body>
</html>Output :
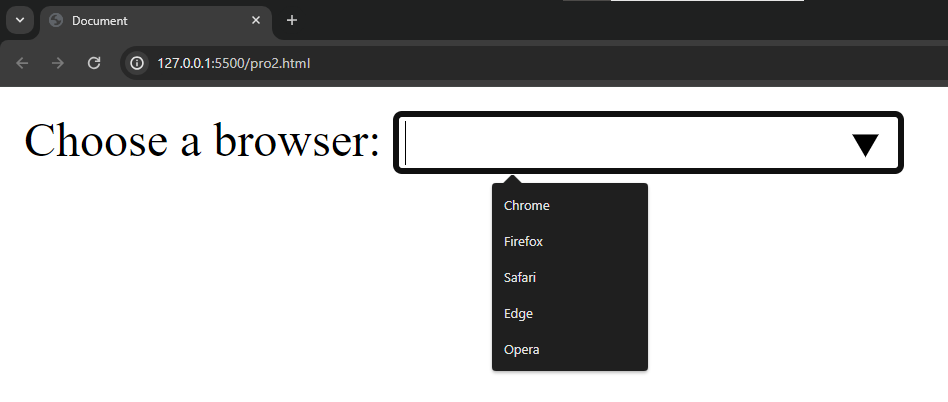
When we move curser to the input box a predefined list is show. Like this
Uses of <datalist> tag :
The ‘<datalist>‘ element in HTML is commonly used to enhance user input by providing a pre-defined list of options that can be associated with an ‘<input>‘ element. Here are some common use cases for the ‘<datalist>‘ element :
1. Autocomplete: One of the primary use cases for <datalist> is to provide autocomplete suggestions for user input. This is useful when you have a predefined set of options, such as a list of countries, cities, programming languages, etc. Users can start typing, and the browser will suggest options from the ‘<datalist>‘.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<label for="countries">Choose a country:</label>
<input list="country-list" id="countries" name="country" />
<datalist id="country-list">
<option value="USA">
<option value="Canada">
<option value="UK">
<!-- More country options -->
</datalist>
</body>
</html>2. Improved User Experience: ‘<datalist>‘ enhances the user experience by reducing the likelihood of input errors. Users can choose from a list of valid options, preventing typos or mistakes.
3. Data Validation: When used in combination with JavaScript, the ‘<datalist>‘ element can be part of a validation mechanism to ensure that the user’s input matches one of the predefined options.
4. Search Suggestions: In search boxes or form fields where users enter search queries, ‘<datalist>‘ can be employed to suggest popular or relevant search terms as the user types.
5. Product or Service Selection: For e-commerce websites, the ‘<datalist>‘ element can be used to provide a list of available products or services, facilitating easy selection by users.
6. Multi-Step Forms: When building multi-step forms, ‘<datalist>‘ can be employed to offer options for certain fields, making it more user-friendly and reducing the likelihood of form abandonment.
Remember that the ‘<datalist> ‘element doesn’t handle the data processing or server-side validation; it is a client-side feature that aids in presenting predefined options to users. Developers often use it in conjunction with JavaScript or server-side logic to handle user input and perform necessary actions based on the selected values.
