Introduction
The <meter> element in HTML is used to represent a scalar measurement within a known range. It’s typically displayed as a horizontal bar, where the filled portion indicates the current value relative to the minimum and maximum values defined for the meter.
Here’s an example of how the <meter> element can be used:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Storage Used: <meter value="60" min="0" max="100">60%</meter></p>
</body>
</html>Output :
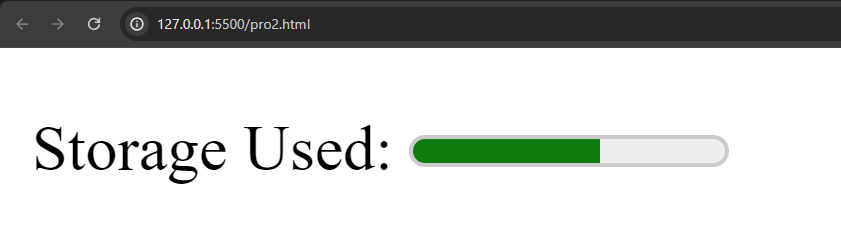
In this example:
- The
<meter>element is used to represent the amount of storage used. - The
valueattribute specifies the current value, which is set to 60 in this case. - The
minandmaxattributes define the minimum and maximum values of the range. Here, the minimum is 0 and the maximum is 100, indicating a percentage range. - The text “60%” inside the
<meter>element is the fallback content, which is displayed if the browser does not support the<meter>element or if the value is not within the specified range.
The appearance of the meter may vary depending on the browser and CSS styling. However, it generally consists of a horizontal bar with a shaded portion representing the current value relative to the range defined by the min and max attributes.
The <meter> element can also have optional attributes such as low, high, and optimum to define thresholds within the range, which can be used for styling or accessibility purposes. Additionally, it can be styled using CSS to customize its appearance further.
