Introduction
The <textarea> element in HTML is used to create a multi-line text input field, allowing users to enter longer-form text or comments. It’s commonly used in forms where users need to input larger amounts of text, such as messages, reviews, or descriptions.
Here’s a basic example of how you might use the <textarea> element:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<label for="message">Message:</label>
<textarea id="message" name="message" rows="4" cols="50">
Lorem ipsum, dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Odit ratione at pariatur minus iure eveniet, dolore dolores, laudantium quae laborum delectus hic maxime? Sunt architecto culpa necessitatibus quaerat sequi delectus
</textarea>
</body>
</html>Output :
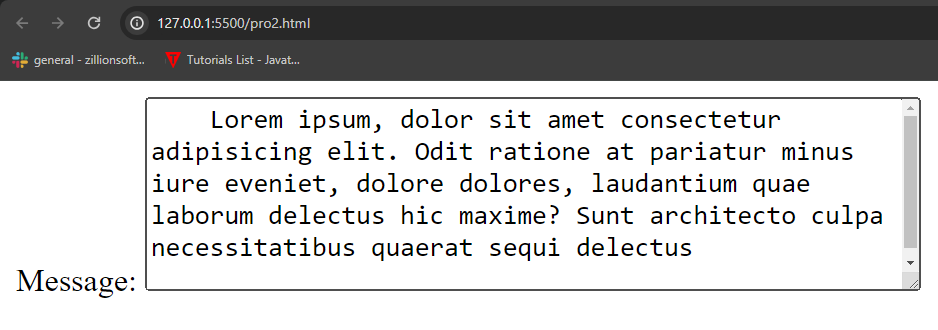
In this example:
- The
<textarea>element has anidattribute (message) that associates it with the<label>element. - It also has a
nameattribute (message), which is used when submitting the form data to the server. - The
rowsandcolsattributes determine the initial size of the text input area in terms of rows and columns.
When the form containing the <textarea> element is submitted, the value entered by the user (or modified by the user) within the <textarea> will be sent to the server along with other form data.
The <textarea> element is useful for capturing longer-form user input and provides a more user-friendly interface compared to single-line input fields for longer text entries.
